Click here to buy secure, speedy, and reliable Web hosting, Cloud hosting, Agency hosting, VPS hosting, Website builder, Business email, Reach email marketing at 20% discount from our Gold Partner Hostinger You can also read 12 Top Reasons to Choose Hostinger’s Best Web Hosting
Spreadsheets are the backbone of business operations, but turning messy feedback, inconsistent imports, or long notes into structured, repeatable insights still eats hours every week. That’s painful when decisions depend on fresh data and tight deadlines. The excel copilot function explained in this post is your practical fix: Microsoft’s new =COPILOT formula lets you write natural-language prompts inside cells so AI runs where your data lives, updating results automatically and collapsing long export-analyze-import cycles into a single, auditable workflow. Click here to learn what exactly do you get with Microsoft Office Home
You can click on advanced Excel tools that can take your skills to the next level.
What the Excel COPILOT function does
In-cell AI: COPILOT is a native Excel function that accepts natural-language prompts and optional cell/range references, and returns generated or structured results directly in a cell. You can treat it like any other formula and combine it with Excel logic.
Common tasks: classification (sentiment, tag), summarization, structured extraction (name, phone, city), and plain-English explanations of formulas.
Access & rollout: Microsoft is rolling Copilot features via Microsoft 365 and the Insider/Beta channels; use typically requires Copilot licensing and files saved to supported cloud locations (OneDrive/SharePoint) for some Copilot experiences.
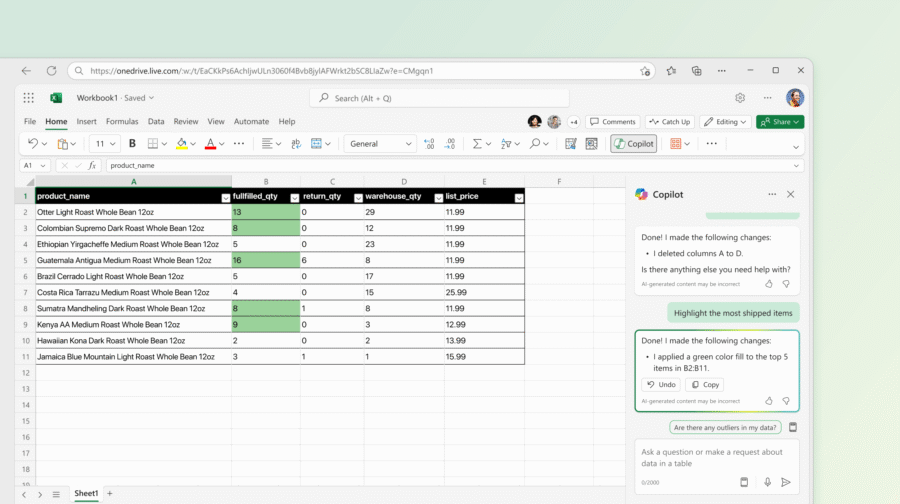
How to use COPILOT in real spreadsheets
Note: adapt prompts for your language and business rules. The=COPILOT function is best used with clear output constraints (e.g., “Return: Positive | Neutral | Negative”).
Example 1 — Sentiment tagging (Customer feedback)
Goal: Turn column A (feedback) into a sentiment tag in column B.
Formula:
B2: =COPILOT(“Classify the sentiment of the comment in A2 as Positive, Neutral, or Negative.”)
Why it works: COPILOT can reference cell content and returns a short label you can COUNTIF() and visualize. Use this for rolling NPS or weekly surveys.
Example 2 — Extract structured data from messy text
Goal: Split a blob of text into Name, Phone, City.
Formula idea:
B2: =COPILOT(“Extract Name, Phone, City from the text in A2 and return as ‘Name|Phone|City’.”)
Then apply TEXTSPLIT(B2,"|") to distribute values into separate columns. This is faster than regular expressions for ad-hoc imports.
How to Merge Cells in Excel
Example 3 — Auto executive summary
Goal: Generate a live plain-English summary of a table A1:D20.
Formula:
E1: =COPILOT(“Summarize the top 3 anomalies and suggested actions in the table A1:D20.”)
The output becomes a one-cell executive note you can paste into reports — and it refreshes if the data changes.
Example 4 — Explain a complex formula
Goal: Help a junior analyst understand a nested formula:
F1: =COPILOT(“Explain what the formula in D3 does and suggest a shorter alternative.”)
Great for learning and code review sessions.
Prompt engineering tips for reliable outputs
Be explicit about format: “Return exactly one of — Positive, Neutral, Negative.”
Use structure for downstream parsing: Ask Copilot to return JSON or pipe-delimited text if you plan to split.
Include fallbacks: “If uncertain, return ‘Unclear’” reduces hallucinations.
Limit scope with ranges: Reference only the cells needed — smaller context = fewer surprises.
Microsoft Announces DeepSeek R1 is Coming to Copilot+ PCs: What You Need to Know
Governance, limits, and compliance (what IT should check)
Licensing: Copilot features are tied to Microsoft 365 Copilot plans and Insider/Beta channel rollouts. Coordinate licensing before scaling.
Storage & access: Certain Copilot features expect files in OneDrive/SharePoint with AutoSave. Verify your retention and DLP settings.
Rate limits & safe uses: Microsoft documents usage patterns and guards; treat COPILOT outputs as assistive, and add validation checks for financial or legal decisions.
Limitations — what COPILOT is not
Not a replacement for heavy ETL: For high-volume, scheduled cleansing or guaranteed transformations, Power Query or dedicated ETL still wins.
Not a numerical calculator: COPILOT is built for language generation and structure — rely on core Excel for deterministic numeric formulas.
Possible ambiguity: When prompts are vague, COPILOT can produce inconsistent results; add tests and guardrails.
Pilot checklist — 6 steps to a low-risk rollout
Identify pilot dataset: customer feedback, support tickets, or contact cleanses.
Confirm licensing & channel access: ensure Copilot license + Beta/Insider access as needed.
Create a prompt library: standardize prompt phrasing and expected outputs in a central sheet.
Add validation rules: sample and manual-review the first 50–100 outputs.
Set governance: document permitted data types and who can use COPILOT.
Measure time savings: track hours saved via the pilot and refine prompts.
 Excel Tips & Tricks QuickStudy Laminated Reference Guide
Excel Tips & Tricks QuickStudy Laminated Reference Guide
Excel Tips & Tricks at your fingertips in 6 laminated pages.
A handy resource for beginning, intermediate or advanced Excel users, this 3-panel (6-page) guide is jam-packed with information and helpful, time-saving hints on Microsoft’s award-winning spreadsheet software. Featuring easy-to-see screen captures and icons, this guide is an ideal next-to-the-monitor reference.
Key Takeaways
Excel COPILOT is a native formula that brings natural-language AI into cells, changing how we classify, summarize, and clean data.
Because it’s a function, outputs recalc automatically when inputs change — ideal for live dashboards and rolling datasets.
Immediate wins include sentiment tagging, field extraction, and live executive summaries.
Governance matters: confirm Copilot licensing, file location rules, and add validation for critical decisions.
FAQs (People Also Ask)
Q: What is the exact syntax of the COPILOT function?
A: COPILOT accepts natural-language prompt parts and optional cell/range references. Example usage is =COPILOT("Classify the text in A2", A2). See Microsoft’s Tech Community blog for examples.
Q: Do I need a special license to use Copilot in Excel?
A: Some Copilot features require Microsoft 365 Copilot licensing and may appear first in Beta/Insider channels; confirm with your tenant admin.
Q: Will Copilot replace Excel formulas?
A: No — Copilot complements Excel. Use it for language tasks, classification, and summaries; rely on core formulas for deterministic numeric calculations.
Q: Can Copilot access internet data or private company docs automatically?
A: Copilot primarily works on the data you provide in the workbook. Some integrations require file placement in OneDrive/SharePoint and admin configuration. Check Microsoft documentation for specifics.
7 Websites to Download Professional Free Excel Templates Spreadsheets
Conclusion
The excel copilot function explained here shows why Microsoft’s =COPILOT is more than a novelty: it converts natural language into structured, live spreadsheet intelligence. For teams that want faster insights without complex ETL, COPILOT offers immediate value — provided you pair it with governance, prompt discipline, and a small pilot. Try the sample prompts above in a test workbook, capture accuracy metrics, and scale where it reliably saves time.
Call to action: Want a ready-to-use prompt library and a test workbook? I’ll build a downloadable sample sheet with the formulas above and validation rules for your team. Also check our SmashingApps coverage for more Excel AI tips.
Official sources referenced
Microsoft Tech Community — Bring AI to your formulas with the COPILOT function in Excel. TECHCOMMUNITY.MICROSOFT.COM
Microsoft Support — Get started with Copilot in Excel. Microsoft Support
Now loading...